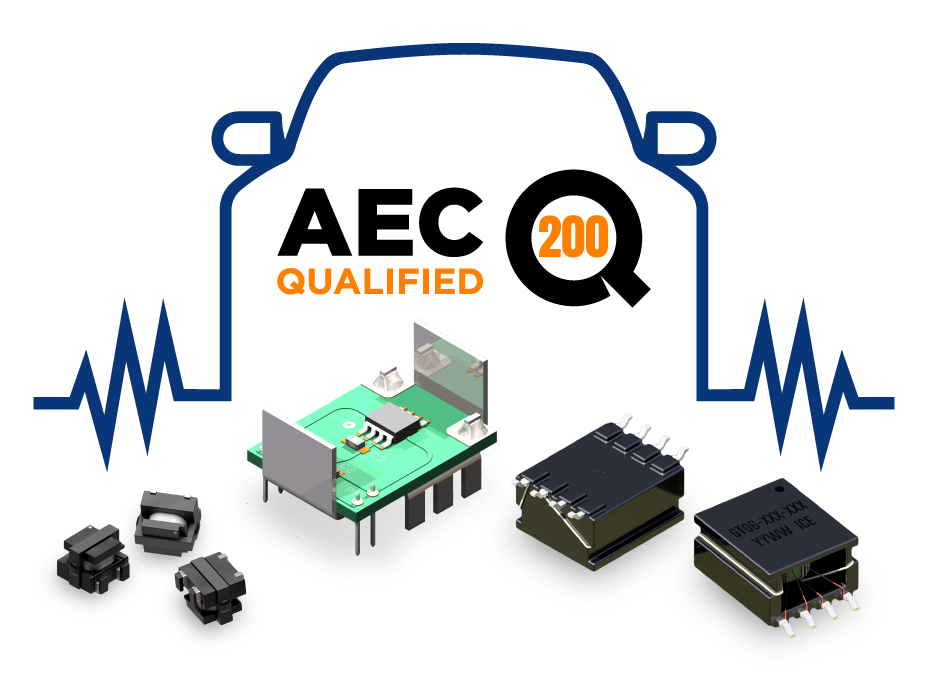
In this article, we take a closer look at AEC-Q200 qualified components and examine their influence on the overall performance of vehicle systems.
 What is AEC?
What is AEC?
The Automotive Electronics Council (AEC) was initially formed by Chrysler, Ford, and GM with the aim of creating standardized part-qualification and quality-system standards. Since its inception, the AEC has maintained two key committees: the Quality Systems Committee and the Component Technical Committee. Today, these committees include representatives from Sustaining Members (such as Aptiv, BorgWarner, Bosch, Bose Corporation, Continental Corporation, Cummins, Delta Energy Systems, Denso International America, Gentex Corporation, Harman, Hella, John Deere Electronics Solutions, Joyson Safety Systems, Kostal Automotive, Lear Corporation, Magna Electronics, Magneti Marelli, Sirius XM, Thyssenkrupp Automotive Technology, Valeo, Veoneer, Visteon Corporation, Vitesco Technologies, and ZF), as well as other Technical, Associate, and Guest Members.
The AEC Component Technical Committee serves as the standardization body responsible for defining rigorous standards for reliable, high-quality electronic components. Components meeting these specifications are deemed suitable for use in the demanding automotive environment without requiring additional component-level qualification testing. The AEC’s website provides direct access to the technical documents developed by the Component Technical Committee.
What is AEC-Q200 Qualification?
AEC-Q200 defines the crucial stress-based qualification requirements and specifies the necessary test conditions for certifying passive electrical components, including inductors and transformers. The aim of this specification is to verify that the component can successfully pass the designated tests, thereby ensuring a certain level of quality and reliability when used in automotive applications.
AEC-Q200 qualification doesn’t come with official certificates or a certification board. Instead, each component supplier follows AEC documents, takes customer requirements into account, and submits data to verify compliance with AEC-Q200 standards. When the test results are successfully completed and documented according to the requirements, a supplier can rightfully claim that the component is “AEC-Q200 Qualified.” It’s like getting a golden stamp of approval for automotive toughness!
What is an AEC-Q200 qualified inductor or transformer?
An AEC-Q200-qualified inductor or transformer has successfully met the rigorous environmental stress testing criteria outlined in the AEC-Q200 global standard. This standard assesses the capability of passive electronic components to endure the temperature extremes and physical demands of automotive environments. Automotive industry companies specifically seek out AEC-Q200 qualified components. Opting for AEC-Q200 qualified components eliminates the necessity for additional component-level qualification testing.
The AEC acknowledges a minimum temperature of −40°C to +85°C. Beyond this range, individual manufacturers take responsibility for developing, testing, and rating their components (such as those rated for 105°C and 125°C ambient temperatures).
The comprehensive AEC-Q200 REV E base PDF document titled “Stress Test Qualification for Passive Components” is available for free download from the AEC Council website.
What AEC-Q200 tests apply to ICE’s off-the-shelf components?
The Table 5 of AEC-Q200 Rev E (March 20, 2023) outlines the test methods and supplementary criteria specifically for magnetics—covering inductors and transformers. These tests encompass various approaches to evaluate the components’ resilience under challenging conditions, including:
🗹 High Temperature Exposure (Storage)
🗹 High-Temperature Operating Life
🗹 Temperature Cycling
🗹 Humidity Bias
🗹 Mechanical Shock
🗹 Vibration
🗹 Terminal Strength (Leaded)
🗹 Resistance to Solvents
🗹 Resistance to Soldering Heat
🗹 Electrostatic Discharge – Human Body Model
🗹 Solderability
🗹 Flammability
🗹 Board Flex
🗹 Terminal Strength (SMD)
In the evaluation of AEC-Q200 qualified components, representative component samples undergo thorough inspection. Their physical dimensions are meticulously measured to ensure alignment with datasheet specifications. Additionally, visual inspections assess construction quality, marking accuracy, and workmanship. Furthermore, electrical parameters are measured both before and after stress testing to confirm adherence to specifications. This rigorous testing regimen provides assurance that these components can withstand the demanding conditions of the automotive environment.
What types of AEC-Q200 components does ICE manufacture?
ICE Components designs and manufactures a broad range of off-the-shelf surface mount devices (SMD) and through hole technology (THT) components that are AEC-Q200 qualified inductors and inductive components, including:
🗹 Current Sense Transformers
🗹 Gate Drive Transformers
🗹 Current Sensors
While the primary purpose of AEC-Q200 is to guarantee robustness in components for automotive applications, it is not typically tailored for non-automotive purposes. There may be alternative components available specifically for non-automotive use. Although these inductors do not fulfill all AEC-Q200 qualification criteria, they are still qualified to meet ICE Components’ commercial standards.
If you have commercial or industrial application requirements, feel free to reach out to ICE Components Technical Support.
ICE Components Qualified Components
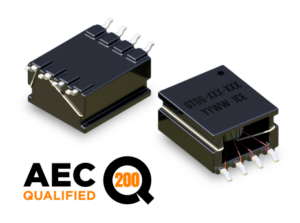 GT06 Gate Drive Transformer
GT06 Gate Drive Transformer
• Height: 7.5mm (Max)
• Footprint: 16.0mm (Ref) x 11.0mm (Max)
• Frequency Range: 40 kHz to 350 kHz
• Creepage/Clearance: 12.5mm
• Suitable for Pick & Place Applications
• Applications include Signal transformer across isolation barrier,
AC/DC & DC/DC converters and isolated gate drivers